Key takeaways: Testicular mesothelioma is the rarest manifestation of mesothelioma, and presents with symptoms similar to a hernia or testicular cancer. Symptoms include localized swelling, lumps on the scrotum, pain in groin, and even abdominal pain or swelling. Because these are non-specific symptoms, it’s imperative to let your doctor know if you’ve had known exposure to asbestos. Treatment for testicular mesothelioma is often multimodal, or a combination of different approaches. Usually, the first course of action is surgical intervention; from there, chemotherapy or radiation are used to ensure that all of the cells have been killed or removed.
Testicular mesothelioma vs. pleural mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma is the most common manifestation (~60-70% of mesothelioma cases) of mesothelioma, in which the lining of the lungs is impacted. Pleural impact is the most common origin site because asbestos usually occurs via inhalation: airborne asbestos fibers easily get trapped within the airways. However, in rarer cases, these asbestos fibers can migrate to and become embedded in more distant areas of the body, like the testes. Testicular mesothelioma accounts for approximately 1-2% of all diagnosed mesothelioma cases—when taking into account the already rare instance of mesothelioma, testicular origins are exceptionally rare. Oftentimes, testicular mesothelioma gets misdiagnosed as a hernia or another more common cancer, like testicular cancer. It’s imperative to spread awareness about the manifestations, symptoms, and treatment options for testicular mesothelioma, as a correct diagnosis (and subsequent treatment) increases patient prognosis.
The symptoms for testicular mesothelioma include:
● Pain in the groin/testes
● Physical irregularity, mimicking a hernia
● Excess fluid buildup
● Swelling of the testes
● Abdominal pain or swelling
● Lump(s) on scrotum
Again, these symptoms are synonymous with other diseases and cancers afflicting the testes. If you have known exposure to asbestos, though, be sure to tell your doctor—this information is critical in differentiating between diseases that present similarly.
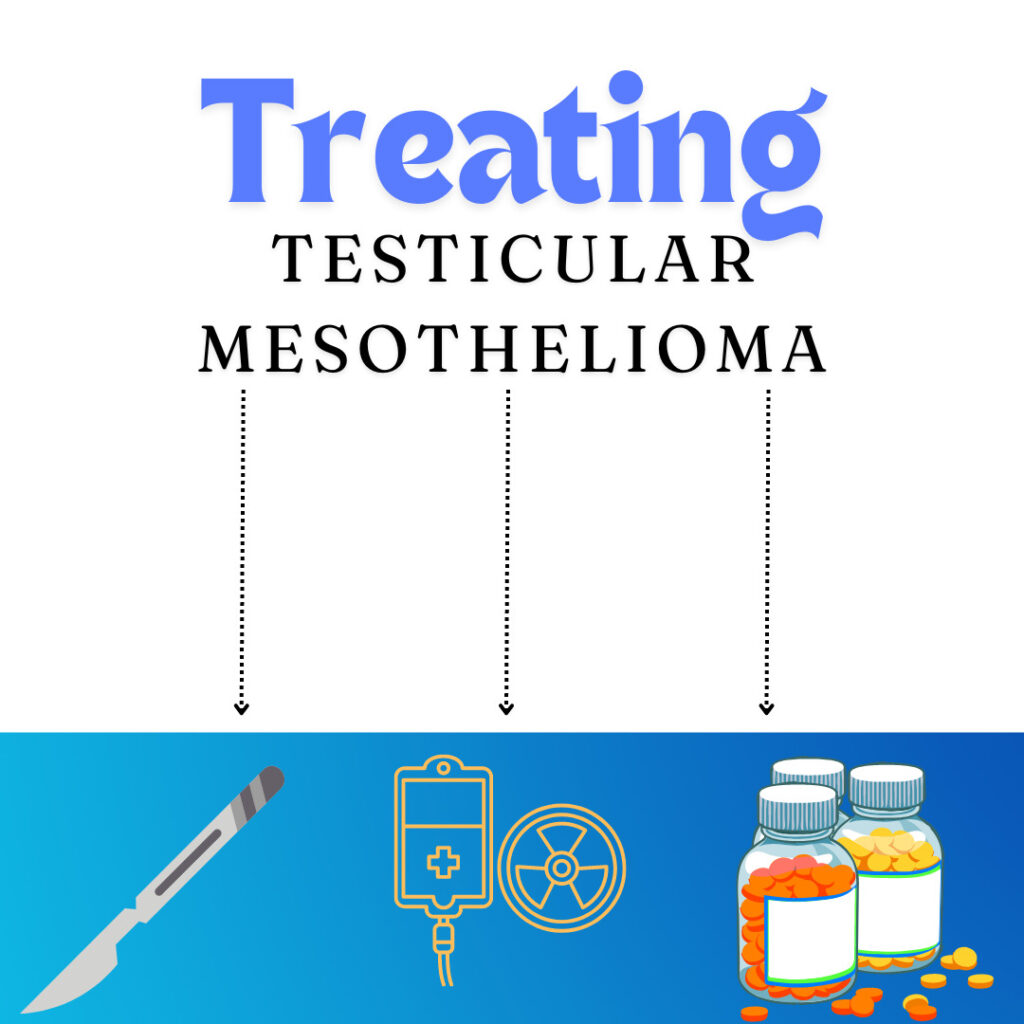
Treatment options for testicular mesothelioma
Although it’s rare—and therefore, difficult to diagnose—testicular mesothelioma is somewhat easier to treat as compared to pleural mesothelioma. There are fewer instances of metastasis, or migration of cancerous cells to other parts of the body; depending on the stage, though, the cancer might spread to lymph nodes or surrounding tissues. But, like pleural mesothelioma, there is no cure for testicular mesothelioma. However, the median overall survival rate is about six years for testicular-based cases, compared to the survival rate of about one year for pleural-based cases. Testicular mesothelioma—although rarer—is known to be more receptive to treatments.
Usually, the first course of action is resection—or surgical intervention—by way of testicular removal. Although an aggressive primary tactic, testicular removal (formally called a radical inguinal orchiectomy) ensures that the bulk of the cancer is totally removed, which reduces the chances of metastasis or remission. Next, depending on how receptive the patient is to surgery, doctors will often opt for radiation or chemotherapy to ensure that all of the mesothelioma cells have been killed. The use of multimodal treatment, or a combination of different types of treatment, is almost always the most effective course of action.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma or another asbestos-related disease, please call 1 (800)-505-6000 or fill out our form. We are here to help you navigate the legal process of filing a claim to receive compensation for your mesothelioma diagnosis. We help mesothelioma victims and their families in Pennsylvania.
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3529728/